UNH Research Center Releases 2021 Global Social Franchise Index
The Global Social Franchise Index, an annual index developed by Paul College's Rosenberg International Franchise Center (RIFC), ranks 131 countries according to the impacts social entrepreneurship and social franchising can have on the well-being of their populations. The index incorporates country metrics that include people’s health conditions, education levels, incomes, and population size, as well as the riskiness of operating in that country. Risks taken into account include political, economic, legal and regulatory risks, as well as geographic distance and cultural distance. The lower the risks of operating in a given country, the more likely these business models can be successful.
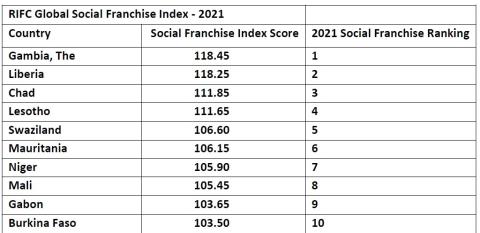
Social entrepreneurship and social franchising can be powerful ways to efficiently alleviate poverty, improve health, provide educational opportunities and improve other social problems for people at the bottom of the pyramid in the most disadvantaged countries identified in the index. The top 10 countries ranked in the 2021 index are all in Africa: Gambia, Liberia, Chad, Lesotho, Swaziland, Mauritania, Niger, Mali, Gabon, and Burkina Faso, in this order.
"These are the countries that may benefit most from social entrepreneurship and social franchising," says Dr. E. Hachemi Aliouche, director of RIFC. To learn more about the Rosenberg International Franchise Center or to view the full list of rankings, visit our website.
